Your Cart is Empty

Forklift Fundamentals: Choosing the Right Model for Your Needs
The Vital Role of Forklifts in Warehousing and Material Handling
Forklifts are the backbone of modern warehouses and material handling operations. Their ability to lift and move heavy loads efficiently not only maximizes productivity but also enhances workplace safety. With the evolution of logistics and supply chains, the role of forklifts has expanded, adapting to varied and complex warehouse environments.
These machines enable precise stacking, rapid loading and unloading, and optimal space utilization, which are crucial in managing the ever-increasing pace and volume of goods that move through distribution centers daily. Forklifts not only facilitate the smooth flow of operations but also help maintain the integrity of goods, reducing damage during handling.
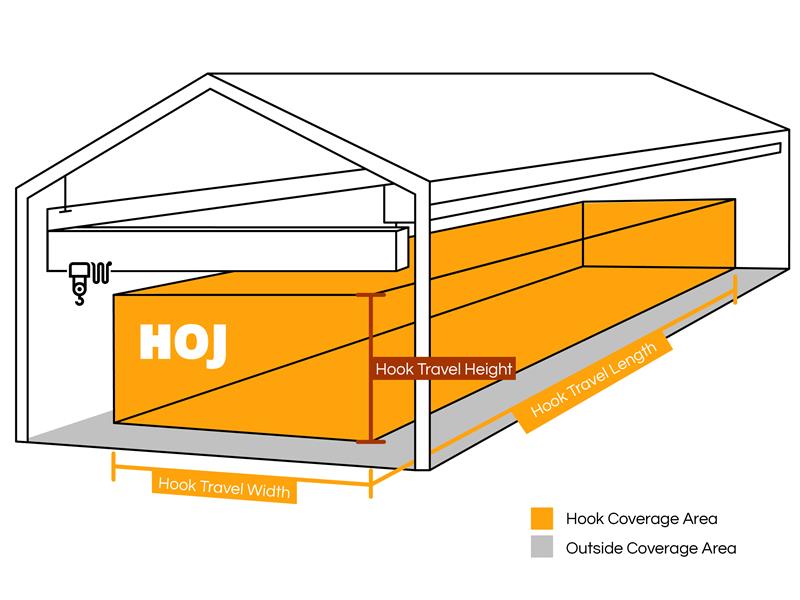
Hoj Innovations has been the leading source or quality forklifts and lift trucks in the Utah area for decades. You can also purchase parts, universal propane tanks, fork extensions and much more right from this website.

Understanding Forklift Types
Not all forklifts are created equally. Understanding the different types available and their specific capabilities is crucial. Each type of forklift is designed to excel in certain environments and tasks. Here’s a closer look at the most common types of forklifts and their optimal uses:
Counterbalance Forklifts
- Description: Counterbalance forklifts are the most common type of forklift. They feature forks at the front and a weight at the back to counterbalance the load. They come in both electric and internal combustion variants.
- Advantages: These forklifts are straightforward to operate and can be used in a variety of settings. They don't require outriggers, allowing the operator to drive up to the exact location of the load or racking.
- Typical Uses: Ideal for lifting and transporting loads in warehouse environments, loading docks, and other industrial settings.
Reach Trucks
- Description: Reach trucks are designed for warehousing operations that require high stacking in narrow aisles. They have two outer legs that distribute the load weight, with a pair of reaching forks that extend to reach the cargo.
- Advantages: Excellent for maximizing storage in warehouses as they can reach high up and fit in tight spaces. Their ability to extend their forks beyond the compartment allows them to reach into racking.
- Typical Uses: Best suited for indoor use, particularly in warehouses with narrow aisles and high shelves.
Pallet Jacks (Manual and Electric)
- Description: Pallet jacks are the simplest form of a forklift, designed to lift and move pallets within a warehouse. They can be either manual or powered.
- Advantages: Highly maneuverable and easy to use, making them perfect for retail environments and light warehousing. Electric models offer ease of movement without physical strain.
- Typical Uses: Ideal for moving goods over short distances such as in supermarkets, small warehouses, or loading areas.
Rough Terrain Forklifts
- Description: Rough terrain forklifts are built to operate in uneven and rugged environments. They typically feature robust, pneumatic tires that can handle uneven surfaces and are often powered by diesel.
- Advantages: These forklifts are durable and can handle a variety of outdoor conditions. They are essential for construction sites and outdoor yards where ground conditions are variable.
- Typical Uses: Commonly used in agriculture, construction, and any other outdoor settings where the ground is uneven or rough.
Telescopic Handlers
- Description: Telescopic handlers, or telehandlers, are similar to forklifts but have a boom and extendable arm, making them more akin to a crane than a traditional forklift.
- Advantages: Versatility is a key strength, as they can lift loads to great heights; they can be equipped with various attachments, such as buckets or lift tables.
- Typical Uses: Used extensively in agriculture and industry where they need to handle a range of tasks like lifting heavy loads to high places, such as in construction or large-scale warehousing.
By understanding these different types of forklifts and their specific applications, businesses can make more informed decisions about which model best suits their operational needs and environment.

Assessing Your Needs
Choosing the right forklift is critical for enhancing operational efficiency and safety. It's important to assess various factors that can influence which forklift model is best suited to your specific requirements. Here are some key considerations:
Type of Materials Being Handled
- Considerations: The physical characteristics of the materials you're handling (such as weight, size, and shape) can significantly impact your choice of forklift. For example, delicate or irregularly shaped items may require specialized attachments or forklifts with enhanced stability features.
- Impact: Selecting a forklift that matches the material handling needs ensures safety, reduces the risk of product damage, and increases the efficiency of operations.
Warehouse Layout and Space Constraints
- Considerations: The design and layout of your warehouse directly influence the type of forklift suitable for the environment. Tight aisles, varied floor conditions, and ceiling height can restrict the maneuverability and size of the forklift you choose.
- Impact: Opting for a forklift that is well-suited to navigate your specific warehouse layout (like narrow-aisle forklifts or those with high maneuverability) can maximize space utilization and streamline workflows.
Load Capacity and Lift Height Requirements
- Considerations: The maximum weight and height at which the forklift must operate are critical factors. These parameters determine the strength and stability required of the forklift.
- Impact: Ensuring that the forklift can handle the maximum load and reach the necessary heights is vital for preventing accidents and maintaining efficient operations.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Usage
- Considerations: The environment in which the forklift will be used affects many aspects of its design. Indoor use typically requires forklifts with non-marking tires and lower emissions, whereas outdoor use may require more robust tires and greater power to navigate rough terrain.
- Impact: Choosing a forklift that is suited to the operating environment ensures longevity of the equipment, compliance with safety regulations, and effectiveness in handling tasks.
Importance of Evaluating Current and Future Business Needs
- Considerations: Anticipating future changes in your business can help you choose a forklift that will not only meet your current needs but also adapt to future growth. This might include considerations for scalability, potential changes in product lines, or expansions in warehouse size.
- Impact: A foresighted approach in selecting a forklift can safeguard against future obsolescence and support business growth without the need for immediate reinvestment in new equipment.
By taking the time to thoroughly assess these factors, businesses can ensure that they invest in a forklift solution that optimizes their operations, addresses all practical requirements, and delivers long-term value. This strategic approach helps in aligning with operational goals and adapting to the dynamic demands of warehousing and material handling.
Key Features to Consider
When selecting a forklift, there are several critical features to consider that can significantly impact safety, operational efficiency, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here’s a detailed look at these essential considerations
Safety Features
- Cameras and Sensors: Modern forklifts can be equipped with cameras and sensors that enhance visibility and safety. Cameras help operators see blind spots or monitor rear views without needing to twist uncomfortably, while sensors can detect proximity to objects or personnel to prevent collisions.
- Ergonomic Designs: Ergonomics play a vital role in operator comfort and safety. Features such as adjustable seats, controls within easy reach, and minimized vibration reduce operator fatigue and the risk of injuries. This is crucial for operations where forklifts are used extensively.
- Impact: Implementing these safety features can significantly reduce workplace accidents and improve productivity by ensuring operators are less fatigued and more alert.
Fuel Options
- Electric: Electric forklifts are ideal for indoor use due to their zero emissions. They are quieter and typically have lower operating costs. They're suitable for environments where air quality is a concern.
- Diesel, Gas, Hybrid: Internal combustion forklifts, including diesel and gas models, are powerful and suitable for outdoor use or in ventilated spaces. Hybrid models offer a balance between electric efficiency and the power of internal combustion models.
- Impact: The choice of fuel impacts not only the operational cost but also the adaptability of the forklift to different environments and working conditions.
Maneuverability and Ease of Use
- Tight Turning Radius: Forklifts designed with a tight turning radius are essential for work in confined spaces. This feature allows for greater flexibility in navigating narrow aisles and tight corners.
- User-Friendly Controls: Intuitive control layouts and responsiveness make forklifts easier to operate and can reduce the learning curve for new operators.
- Impact: Enhanced maneuverability and ease of use can lead to faster task completion and can accommodate a wider range of operators, increasing workforce flexibility.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the frequency and cost of routine maintenance. Electric forklifts generally require less maintenance than their combustion counterparts since they have fewer moving parts.
- Durability: The construction quality of a forklift affects its lifespan and durability. Heavy-duty materials and robust construction help withstand harsh working conditions and reduce the likelihood of frequent repairs.
- Impact: Choosing a forklift with low maintenance needs and high durability can significantly reduce downtime and long-term operating costs.
By carefully evaluating these features, businesses can select a forklift that not only fits their immediate operational needs but also provides a safe, efficient, and cost-effective solution over its operational life. This careful consideration helps in achieving high productivity levels while keeping maintenance and operating costs in check.

Economic Considerations
Choosing the most cost-effective way to incorporate forklifts into your operations involves analyzing several economic factors. From acquisition to operation, different approaches have varied financial implications. Here’s an in-depth look at these considerations:
Cost Comparison Between Purchasing, Leasing, and Renting Forklifts
- Purchasing: Buying a forklift outright is a significant upfront investment but can be more economical in the long term, especially if the equipment is used regularly over many years. Ownership allows for complete control over the machine, including customization and usage without restrictions.
- Leasing: Leasing a forklift can reduce upfront costs, often requiring lower monthly payments than a loan for purchasing. This option also provides flexibility to upgrade to newer models at the end of the lease term, which can be crucial for maintaining technological competitiveness and efficiency.
- Renting: Ideal for short-term needs or seasonal peaks, renting offers the highest flexibility without the commitment of a long-term investment. It also typically includes maintenance, reducing the need to have in-house service capabilities.
- Impact: The choice between purchasing, leasing, and renting will depend on your company’s financial situation, operational demands, and long-term strategic plans. Each option offers different benefits in terms of cash flow management, asset liability, and capital investment.
The Impact of Operational Costs (Maintenance, Fuel, etc.)
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance is crucial for operational efficiency and safety. The costs can vary significantly based on the type of forklift and its usage intensity. Electric forklifts usually incur lower maintenance costs compared to internal combustion models.
- Fuel Costs: Fuel expenses can fluctuate and need to be carefully considered, especially for forklifts that use diesel or gas. Electric forklifts, while potentially more expensive upfront, can offer savings in fuel costs over time, particularly with the increasing efficiency of electric batteries.
- Impact: Operational costs are recurring expenses that can accumulate significantly over the lifespan of the equipment. Efficient management of these costs can lead to considerable savings and a more predictable budget.
Return on Investment Analysis
- Calculating ROI: To determine the return on investment, consider the total cost of ownership (purchase price plus ongoing operational costs) against the productivity gains and cost savings achieved by using the forklift. This includes improved operational efficiency, reduced labor costs, and lower product damage rates.
- Long-Term Value: Evaluate how the forklift contributes to long-term business objectives, such as increased capacity, expansion into new markets, or enhanced service levels.
- Impact: A thorough ROI analysis helps in making an informed decision about which forklift acquisition method aligns best with business goals and financial strategies. It considers not just the immediate costs but also the long-term benefits and savings.
By understanding these economic considerations, businesses can make a strategic decision on how best to integrate forklifts into their operations, balancing between initial expenditures, ongoing costs, and the overall return on the investment. This balanced approach ensures that the chosen strategy supports both current operational needs and future growth ambitions.
Compliance and Regulations
Navigating the compliance landscape is crucial for safe and legal forklift operations. Understanding and adhering to the relevant safety standards, training requirements, and environmental regulations not only ensures legal compliance but also enhances operational safety and efficiency. Here’s a breakdown of these critical elements:
Overview of Relevant Safety Standards and Regulations
- OSHA and ANSI Guidelines: In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) set comprehensive guidelines that govern the operation of forklifts. These standards include specifications on operations, maintenance, and safety equipment.
- Local and International Standards: Different regions may have additional standards that need to be met. Internationally, standards such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) provide guidelines for aspects of forklift design and usage that can affect global operations.
- Impact: Compliance with these safety standards is mandatory and helps prevent accidents and legal issues. It also ensures that forklifts are operated in a manner that preserves the safety of operators and other personnel.
Importance of Operator Training and Certification
- Certification Requirements: OSHA requires that all forklift operators receive proper training and certification before they can legally operate a forklift. This training covers the basics of operation, safety practices, and the specific types of forklifts the operator will use.
- Continuous Education: Refresher training and evaluations are also required at specified intervals or after any accident or observed unsafe operation to ensure continued compliance and safety.
- Impact: Proper training and certification not only comply with legal requirements but significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. They also improve operational efficiency by helping operators understand the best practices and nuances of safe forklift operation.
Environmental Regulations Affecting Forklift Selection (Especially Regarding Emissions)
- Emission Standards: Especially relevant for forklifts powered by internal combustion engines, emission standards aim to reduce the environmental impact of these vehicles. Regulations such as the U.S. EPA's Tier 4 standards for diesel engines are stringent.
- Electric and Hybrid Alternatives: As environmental concerns grow, electric and hybrid forklifts are becoming more popular due to their lower emissions. These options are particularly important in indoor environments or regions with strict air quality regulations.
- Impact: Adhering to environmental regulations not only helps protect the environment but also ensures compliance with legal standards that can affect business operations. Choosing forklifts that meet these regulations can also reduce the company’s carbon footprint and appeal to eco-conscious customers.
Understanding and integrating these compliance and regulatory requirements into your forklift selection and operation processes ensure safe, efficient, and lawful material handling. This not only protects against potential legal and financial penalties but also builds a culture of safety and responsibility within the organization.
The Role of Automation in Forklift Operations
The integration of automation and advanced connectivity technologies in forklift operations is revolutionizing how businesses handle materials and manage warehouses. These technological advancements not only increase efficiency and safety but also offer significant improvements in data collection and operational oversight. Here’s an in-depth look at these developments:
Advances in Forklift Technology (Automation, IoT Connectivity)
- Automation: Automated forklifts, also known as autonomous or self-driving forklifts, can operate without human intervention, navigating warehouses using sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence. These systems can be programmed to follow optimal paths, avoid obstacles, and execute repetitive tasks with high precision.
- IoT Connectivity: Internet of Things (IoT) technology enables forklifts to connect to a central system that monitors and controls operations. This connectivity allows for real-time data collection on vehicle status, load handling, and operator behavior, which can be used to optimize routes, maintenance schedules, and overall fleet management.
- Impact: These technologies reduce the reliance on human operators for routine and repetitive tasks, decrease the likelihood of human error, and allow for more complex and efficient operations management.
Benefits of Integrating Modern Technologies for Enhanced Productivity and Safety
- Enhanced Productivity: Automated forklifts can operate around the clock without fatigue, leading to higher throughput and faster completion of tasks. IoT connectivity allows for the seamless integration of forklift operations with warehouse management systems, resulting in a more synchronized operation where inventory and handling processes are tightly controlled and monitored.
- Increased Safety: Automation significantly reduces the risk of accidents associated with human error. Advanced sensor and camera systems can detect and react to obstacles more quickly than a human operator, thereby enhancing safety. Additionally, IoT enables proactive maintenance alerts which prevent breakdowns and potential hazardous situations.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The data collected through IoT-connected forklifts can provide deep insights into operational efficiencies and bottlenecks. Managers can use this data to make informed decisions about workflow adjustments, training needs, and equipment upgrades, leading to continuous improvement in processes.
- Cost Efficiency: Over time, the investment in automated and IoT-connected forklifts can lead to substantial cost savings. These savings are achieved through optimized resource use, reduced downtime, and minimized labor costs due to the automation of routine tasks.
Implementing Automation in Your Operations
- Pilot Programs: Starting with a pilot program allows a business to test the benefits of automation technology in a controlled manner, assessing the impact on their specific operations before committing to a full-scale rollout.
- Training and Integration: As technologies are introduced, it’s crucial to train staff not just on how to use the new equipment, but also on how to work alongside automated systems, ensuring smooth integration and operation.
By embracing these advanced technologies, companies can significantly enhance the efficiency, safety, and profitability of their forklift operations. Automation and IoT connectivity represent a transformative step in the evolution of material handling, paving the way for more intelligent, responsive, and data-driven warehouse environments.